96 Ramsar Sites in India 2025: Names, State-Wise List
India has 96 Ramsar Sites as of December 2025, maximum in Tamil Nadu. The largest (Sundarban), smallest (Renuka Lake), and newest additions like Kopra Jalashay and Silisereh Lake.
UPSC Prelims
Environment, Ecology, and Biodiversity
Latest Update

Gajendra Singh Godara
Dec 17, 2025
8
mins read
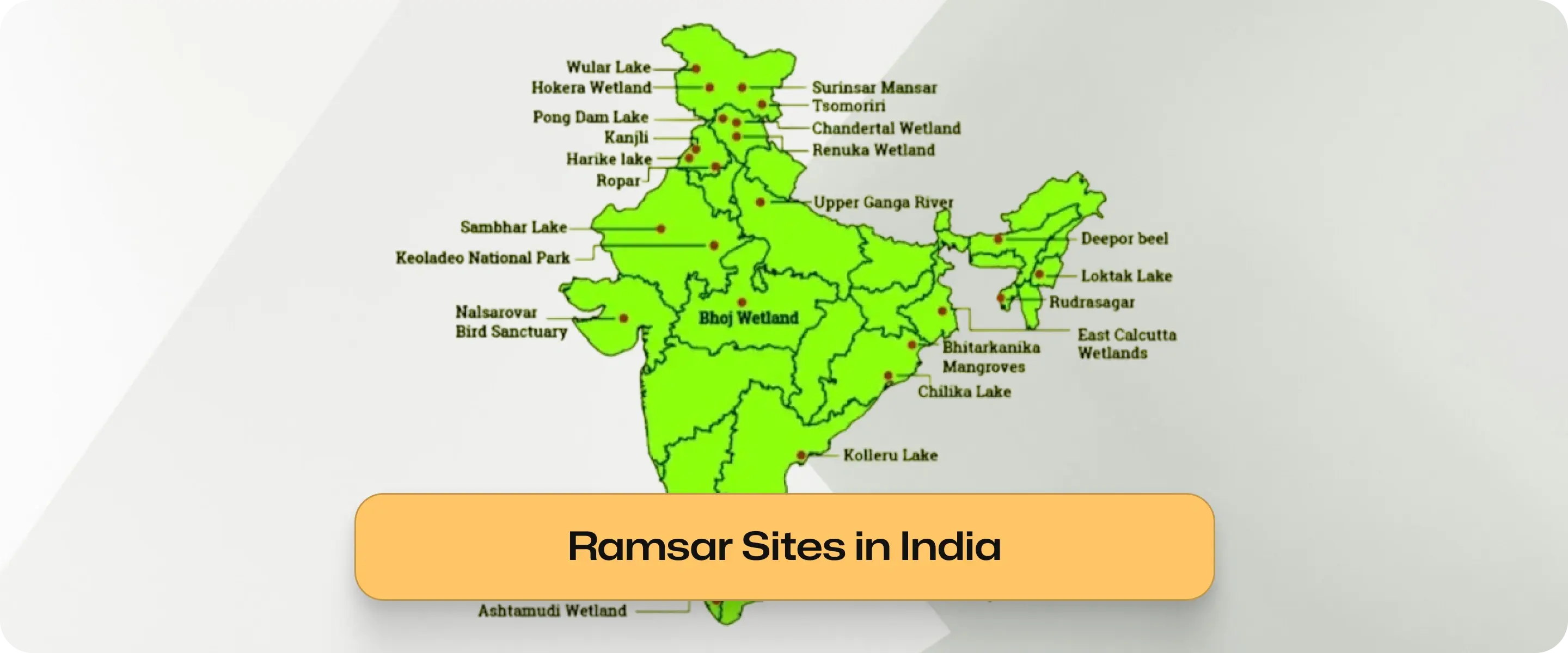
As of December 2025, the total Ramsar Sites in India stands at 96. This expansion reflects India's strategic focus on preserving these biologically rich ecosystems.
Get a clear knowledge of the Ramsar Convention. It includes a state-by-state breakdown and details on the latest additions. This will help you get ready for the upcoming exam cycle.
What is a Ramsar Site?
A Ramsar Site is a wetland designated to be of "international importance" under the Ramsar Convention.
Definition: The convention defines wetlands broadly to include lakes, rivers, swamps, marshes, peatlands, estuaries, deltas, tidal flats, mangroves, and coral reefs. It also encompasses human-made sites such as reservoirs and salt pans.
The Convention: The Ramsar Convention was signed on February 2, 1971, in Ramsar, Iran. This treaty helps countries work together to protect and use wetlands wisely.
India's Participation: India ratified the convention on February 1, 1982. Since then, it has chosen sites that meet specific criteria for international importance. These sites support vulnerable species or sustain 20,000 or more waterbirds.
The Ramsar Convention's main goal is: "To conserve and wisely use all wetlands. This is done through local and national actions, along with international cooperation. It helps achieve sustainable development around the world".
The Montreux Record
This register lists Ramsar Sites where changes in the environment have happened, are happening, or may happen. These changes are because of technology, pollution, or other human activities.
Current Indian Sites: Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) and Loktak Lake (Manipur).
Success Story:Chilika Lake in Odisha was recorded in 1993 because of siltation. It was removed from the record in 2002 after successful restoration efforts.
Join our WhatsApp Community
How Many Ramsar Sites in India?
There are currently 96 Ramsar Sites in India. Tamil Nadu holds the highest number of sites, followed by Uttar Pradesh. This distribution highlights the rich coastal and riverine wetland ecosystems present in the southern and northern plains respectively.
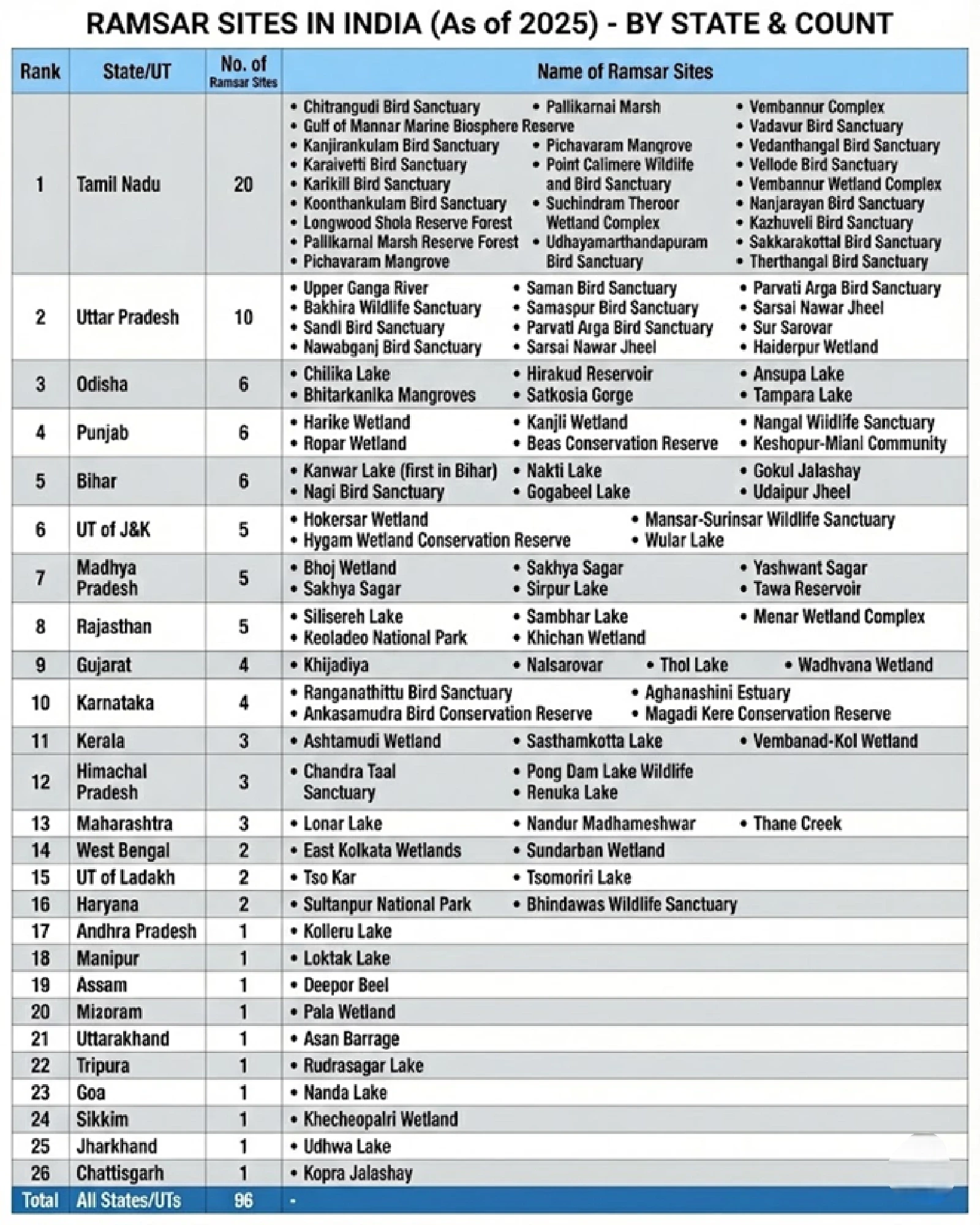
State-wise Number of Ramsar Sites
The following table summarizes the distribution of these wetlands across Indian states:
Rank | State | No. of Ramsar Sites | Name of Ramsar Sites |
1 | Tamil Nadu | 20 |
|
2 | Uttar Pradesh | 10 |
|
3 | Odisha | 6 |
|
4 | Punjab | 6 |
|
5 | Bihar | 6 |
|
6 | UT of J&K | 5 |
|
7 | Madhya Pradesh | 5 |
|
8 | Rajasthan | 5 |
|
9 | Gujarat | 4 |
|
10 | Karnataka | 4 |
|
11 | Kerala | 3 |
|
12 | Himachal Pradesh | 3 |
|
13 | Maharashtra | 3 |
|
14 | West Bengal | 2 |
|
15 | UT of Ladakh | 2 |
|
16 | Haryana | 2 |
|
17 | Andhra Pradesh | 1 |
|
18 | Manipur | 1 |
|
19 | Assam | 1 |
|
20 | Mizoram | 1 |
|
21 | Uttarakhand | 1 |
|
22 | Tripura | 1 |
|
23 | Goa | 1 |
|
24 | Sikkim | 1 |
|
25 | Jharkhand | 1 |
|
26 | Chattisgarh | 1 |
|
Total | All States/UTs | 96 |
New Ramsar Sites in India
For UPSC 2026 aspirants, the sites added in the last 12-18 months are critical for Prelims. The Commission often frames matching-list questions based on these recent designations.
New Additions in 2025
Several sites from Bihar, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu were designated this year, adding significant value to India's conservation network.
Silisereh Lake (Rajasthan): A man-made lake in Alwar, Rajasthan. Maharaja Vinay Singh built it in 1845. The city created the lake to supply water. Authorities recently named this area India's 96th Ramsar Site.
Kopra Jalashay (Chattisgarh): A reservoir-type wetland in Chattishgarh, now designated as a Ramsar site. Everyone now recognizes its importance for hydrological and ecological purposes.
Gogabeel Lake (Bihar): A permanent oxbow lake formed by the Mahananda and Kankhar rivers. It was declared Bihar's first Community Reserve in 2019. The site is an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA). It supports species like the Lesser Adjutant Stork and Pallas's Fish Eagle.
Gokul Jalashay (Bihar): This 448-hectare oxbow lake is on the southern edge of the Ganga River. It is home to over 50 bird species. Local communities utilize the wetland for fishing and agriculture.
Udaipur Jheel (Bihar): It covers 319 hectares. This oxbow lake is an important home for local and migratory waterbirds. It is next to the Udaipur Wildlife Sanctuary.
Khichan (Rajasthan): It is in the northern Thar Desert of Rajasthan. It is famous around the world for its large groups of Demoiselle Cranes that come during winter. The site comprises two water bodies—Ratri Nadi and Vijaysagar Talab.
Menar (Rajasthan): This place is called the "Bird Village." It is a freshwater wetland made up of three ponds: Braham Talab, Dhand Talab, and Kheroda Talab. It hosts over 110 species of waterbirds, including the Critically Endangered White-rumped Vulture.
Udhwa Lake (Jharkhand): The only Ramsar site in Jharkhand, this bird sanctuary consists of Patauran Jheel and Berhale Jheel. It connects to the Ganga River through a 25 km channel. It is home to the Critically Endangered Oriental White-backed Vulture.
Significant Additions in 2024
Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka): This estuary is where the Aghanashini River meets the Arabian Sea. It is one of the last free-flowing rivers in Karnataka. It supports rich mangrove vegetation and provides livelihoods through bivalve shell mining.
Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu): The only urban natural "Shola" forest remaining in the Nilgiris. It functions as a "perched aquifer," retaining water and regulating the microclimate for the town of Kotagiri.
Tawa Reservoir (Madhya Pradesh): It is part of the Satpura Tiger Reserve. This man-made reservoir helps support the Indian Giant Squirrel. It is also home to the state fish of MP, the Tor mahseer.
Tawa Reservoir (Madhya Pradesh): Located within the Satpura Tiger Reserve, this human-made reservoir supports the Indian Giant Squirrel and the state fish of MP, the Tor mahseer.
Add as a preferred Source on Google
Ramsar Sites in India: Largest, Smallest, Oldest and Newest
Largest Ramsar Sites in India
India's largest Ramsar sites are big wetland areas. They support many types of plants and animals. These sites are important for global wetland conservation.
These large wetlands cover many states. They provide important homes for migratory birds, aquatic animals, and many land creatures. The largest sites act as important carbon sinks. They also help with water management and provide benefits to local communities.
Rank | Ramsar Site | State | Area (km²) |
1 | Sundarban Wetland | West Bengal | 4,230 |
2 | Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu | 1,513 |
3 | Vembanad-Kol Wetland | Kerala | 1,512.5 |
4 | Chilika Lake | Odisha | 1,165 |
5 | Satkosia Gorge | Odisha | 981.97 |
6 | Kolleru Lake | Andhra Pradesh | 901 |
Smallest Ramsar Sites in India
India also protects several compact wetland ecosystems that, despite their limited geographical footprint, hold immense ecological significance.
Rank | Ramsar Site | State | Area (km²) |
1 | Renuka Lake | Himachal Pradesh | 0.2 |
2 | Vembannur Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu | 0.2 |
3 | Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu | 0.4 |
4 | Nanda Lake | Goa | 0.42 |
5 | Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu | 0.44 |
Oldest Ramsar Sites in India
India's pioneering Ramsar designations date back to the early 1980s, marking the nation's early commitment to international wetland conservation.
Rank | Ramsar Site | State | Year Designated |
1 | Chilika Lake | Odisha | 1981 |
2 | Keoladeo Ghana National Park | Rajasthan | 1981 |
They are also known as First Ramsar Site in India.
Chilika Lake (Odisha) and Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) were jointly designated as India's first Ramsar sites on October 1, 1981. Chilika Lake, a brackish lagoon covering 1,165 km², became the world's second-largest brackish lagoon and supports diverse migratory bird species.
Newest Ramsar Sites in India
Rank | Ramsar Site | State | Year Designated |
1 | Kopra Jalashay | Chhattisgarh | 2025 |
2 | Silisereh Lake | Rajasthan | 2025 |
Ecological Significance of Ramsar Sites in India
Ramsar designation implies a commitment to conservation and specific ecological responsibilities. Understanding these services is vital for writing substantive answers in GS Paper III.
1. Flood Mitigation and Water Regulation
Wetlands function as natural sponges, absorbing surface runoff during heavy rainfall. Pallikaranai Marsh in Chennai illustrates this; its degradation has exacerbated urban flooding. Similarly, the East Kolkata Wetlands treat the city's wastewater and provide flood protection.
2. Carbon Sequestration
Coastal wetlands, such as mangroves and salt marshes, sequester "Blue Carbon" at rates significantly higher than terrestrial forests. Sites like Bhitarkanika and Pichavaram play a crucial role in climate change mitigation by trapping carbon in their sediment layers for millennia.
3. Biodiversity Support
Ramsar sites support species that are often endemic or endangered.
Loktak Lake is the only natural habitat of the Sangai (dancing deer).
Chilika Lake sustains the Irrawaddy Dolphin population.
Upper Ganga River provides habitat for the Gangetic Dolphin and Gharial.
4. Economic Value
Wetlands provide direct economic benefits. For instance, Vembanad Lake supports a large-scale houseboat tourism industry and unique below-sea-level paddy cultivation (Kuttanad). Similarly, the Aghanashini Estuary supports thousands of families through fishing and bivalve collection.
Major Threats to Indian Wetlands and Ramsar Sites in India
Despite their protected status, Indian wetlands face severe anthropogenic pressures.
Urban Encroachment: Expanding cities consume wetland areas for real estate. The Thane Creek Flamingo Sanctuary faces pressure from the surrounding Mumbai metropolitan region.
Pollution: Runoff from agriculture (fertilizers and pesticides) and untreated industrial waste leads to eutrophication. This process depletes oxygen in the water, killing fish and promoting the growth of invasive species.
Invasive Species: Weeds like Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) choke water bodies like Harike and Loktak, disrupting the native food web.
Climate Change: Rising sea levels threaten coastal wetlands like Point Calimere and the Sundarbans with salinity ingress, which can permanently alter freshwater ecosystems.
Frequently asked question (FAQs)
How many Ramsar Sites are there in India 2025?
How many new Ramsar sites were added in India in 2025?
Which state has the most Ramsar Sites in India?
What is the Montreux Record?
Which is India's 96th Ramsar site?
Gajendra Singh Godara brings authentic UPSC preparation insights from his four-attempt journey, having successfully cleared Prelims and written Mains multiple times. His deep expertise spans Polity, Modern History, International Relations, and Economy. At PadhAI, Gajendra transforms his extensive exam experience into accessible content that simplifies complex concepts for aspirants at every preparation stage. His firsthand understanding of UPSC's demands enables him to create targeted materials that save time while maximizing learning efficiency for current affairs, general studies, and optional subjects.












