10-Step UPSC Preparation Guide
The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) Civil Services Examination (CSE) recruits officers for prestigious roles like the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) and Indian Foreign Service (IFS). Success in this rigorous selection process demands a calculated strategy rather than random effort. At PadhAI.ai, we function as your strategic architects, translating the complex examination landscape into a linear, actionable roadmap.
What is the UPSC CSE?
The UPSC Civil Services Examination is a three-tiered assessment designed to test academic expertise and administrative aptitude. Understanding this structure is the first requirement for any serious aspirant.
Preliminary Examination (Prelims): This stage acts as a screening mechanism. It comprises two objective papers: General Studies (GS) Paper I and the Civil Services Aptitude Test (CSAT) Paper II. The CSAT is qualifying, but the GS Paper I score determines your eligibility for the next phase.
Main Examination (Mains): This descriptive phase tests your depth of knowledge. It includes nine papers: four General Studies papers, two optional subject papers, one essay paper, and two language papers.
Personality Test (Interview): The final stage assesses your communication skills, leadership qualities, and mental alertness.
Does the Preliminary Exam score count towards the final rank? No. The Preliminary Exam serves only as a qualification threshold for the Mains.
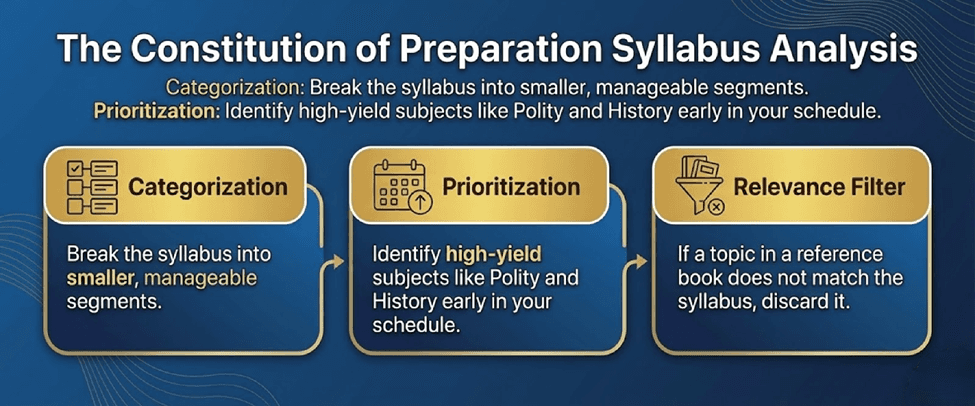
Step 1: The Constitution of Preparation Syllabus Analysis
Aspirants often commit the error of starting their study without defining the boundaries of the curriculum. The syllabus functions as your primary navigation tool. You must study the official syllabus to align every topic you read with the exam requirements.
Categorization: Break the syllabus into smaller, manageable segments.
Prioritization: Identify high-yield subjects like Polity and History early in your schedule.
Relevance Filter: If a topic in a reference book does not match the syllabus, discard it.
As noted by previous toppers, understanding the scope of the syllabus prevents aimless reading and maintains a focused preparation trajectory.
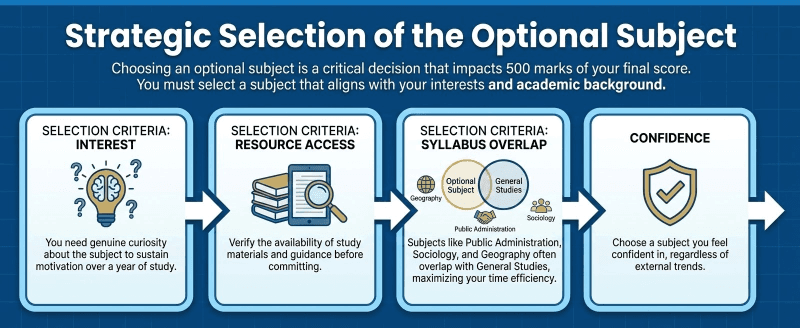
Step 2: Strategic Selection of the Optional Subject
Choosing an optional subject is a critical decision that impacts 500 marks of your final score. You must select a subject that aligns with your interests and academic background.
Selection Criteria:
Interest: You need genuine curiosity about the subject to sustain motivation over a year of study.
Resource Access: Verify the availability of study materials and guidance before committing.
Syllabus Overlap: Subjects like Public Administration, Sociology, and Geography often overlap with General Studies, maximizing your time efficiency.
Confidence: Choose a subject you feel confident in, regardless of external trends.
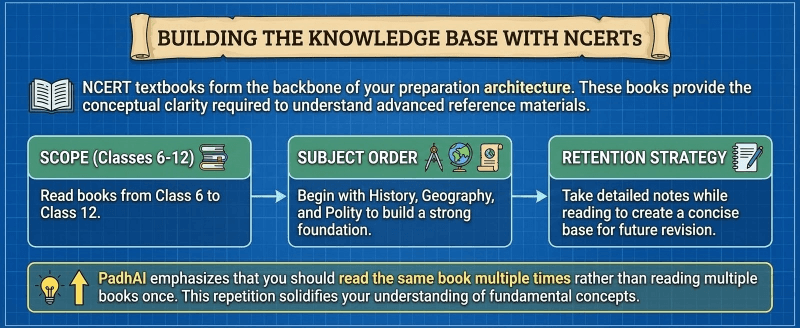
Step 3: Building the Knowledge Base with NCERTs
NCERT textbooks form the backbone of your preparation architecture. These books provide the conceptual clarity required to understand advanced reference materials.
Scope: Read books from Class 6 to Class 12.
Subject Order: Begin with History, Geography, and Polity to build a strong foundation.
Retention Strategy: Take detailed notes while reading to create a concise base for future revision.
PadhAI emphasizes that you should read the same book multiple times rather than reading multiple books once. This repetition solidifies your understanding of fundamental concepts.
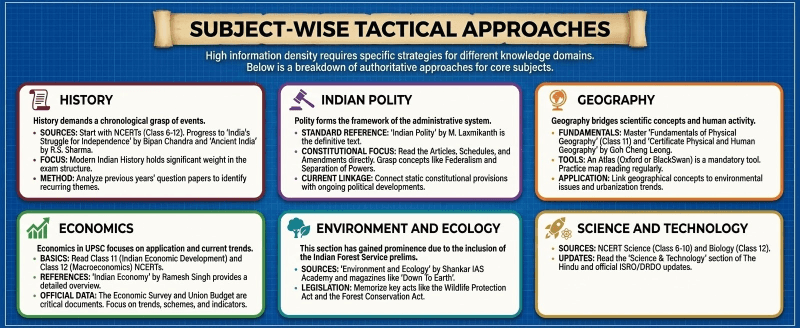
Step 4: Subject-Wise Tactical Approaches
High information density requires specific strategies for different knowledge domains. Below is a breakdown of authoritative approaches for core subjects like General Studies.
History
History demands a chronological grasp of events.
Sources: Start with NCERTs (Class 6-12). Progress to "India's Struggle for Independence" by Bipan Chandra and "Ancient India" by R.S. Sharma.
Focus: Modern Indian History holds significant weight in the exam structure.
Method: Analyze previous years' question papers to identify recurring themes.
Indian Polity
Polity forms the framework of the administrative system.
Standard Reference: "Indian Polity" by M. Laxmikanth is the definitive text.
Constitutional Focus: Read the Articles, Schedules, and Amendments directly. Grasp concepts like Federalism and Separation of Powers.
Current Linkage: Connect static constitutional provisions with ongoing political developments.
Geography
Geography bridges scientific concepts and human activity.
Fundamentals: Master "Fundamentals of Physical Geography" (Class 11) and "Certificate Physical and Human Geography" by Goh Cheng Leong.
Tools: An Atlas (Oxford or BlackSwan) is a mandatory tool. Practice map reading regularly.
Application: Link geographical concepts to environmental issues and urbanization trends.
Economics
Economics in UPSC focuses on application and current trends.
Basics: Read Class 11 (Indian Economic Development) and Class 12 (Macroeconomics) NCERTs.
References: "Indian Economy" by Ramesh Singh provides a detailed overview.
Official Data: The Economic Survey and Union Budget are critical documents. Focus on trends, schemes, and indicators.
Environment and Ecology
This section has gained prominence due to the inclusion of the Indian Forest Service prelims.
Sources: "Environment and Ecology" by Shankar IAS Academy and magazines like "Down To Earth".
Legislation: Memorize key acts like the Wildlife Protection Act and the Forest Conservation Act.
Science and Technology
Sources: NCERT Science (Class 6-10) and Biology (Class 12).
Updates: Read the "Science & Technology" section of The Hindu and official ISRO/DRDO updates.
Step 5: Current Affairs Preparation
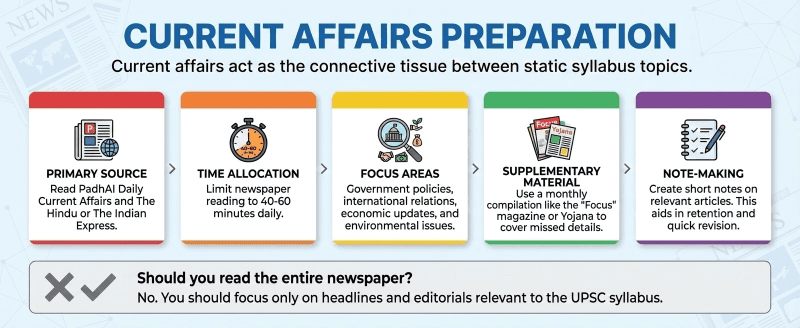
Current affairs act as the connective tissue between static syllabus topics.
Primary Source: Read PadhAI Daily UPSC Current Affairs and The Hindu or The Indian Express.
Time Allocation: Limit newspaper reading to 40-60 minutes daily.
Focus Areas: Government policies, international relations, economic updates, and environmental issues.
Supplementary Material: Use a monthly compilation like the PadhAI monthly magazine for UPSC or Yojana to cover missed details.
Note-Making: Create short notes on relevant articles. This aids in retention and quick revision.
Should you read the entire newspaper? No. You should focus only on headlines and editorials relevant to the UPSC syllabus.
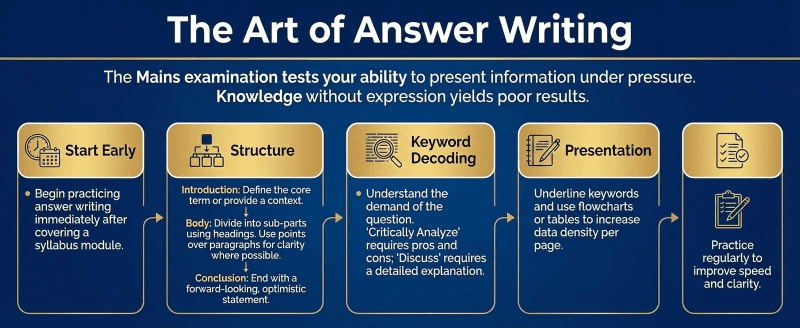
Step 6: The Art of Answer Writing
The Mains examination tests your ability to present information under pressure. Knowledge without expression yields poor results.
Start Early: Begin practicing answer writing immediately after covering a syllabus module.
Structure: Every answer must have an Introduction, Body, and Conclusion.
Introduction: Define the core term or provide a context.
Body: Divide into sub-parts using headings. Use points over paragraphs for clarity where possible.
Conclusion: End with a forward-looking, optimistic statement.
Keyword Decoding: Understand the demand of the question. "Critically Analyze" requires pros and cons; "Discuss" requires a detailed explanation.
Presentation: Underline keywords and use flowcharts or tables to increase data density per page.
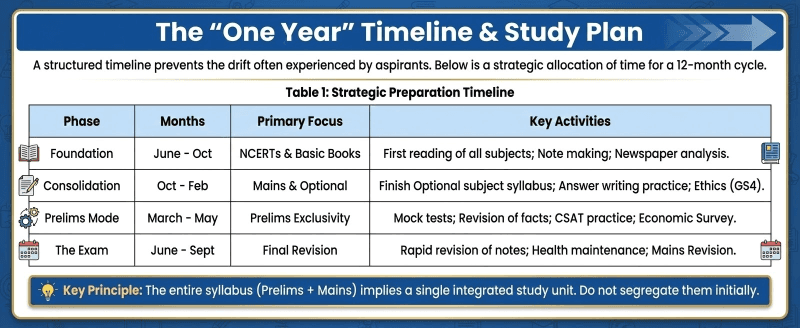
Step 7: The "One Year" Timeline & Study Plan
A structured timeline prevents the drift often experienced by aspirants. Below is a strategic allocation of time for a 12-month cycle.
Table 1: Strategic Preparation Timeline
Phase
Months
Primary Focus
Key Activities
Foundation
June - Oct
NCERTs & Basic Books
First reading of all subjects; Note making; Newspaper analysis.
Consolidation
Oct - Feb
Mains & Optional
Finish Optional subject syllabus; Answer writing practice; Ethics (GS4).
Prelims Mode
March - May
Prelims Exclusivity
Mock tests; Revision of facts; CSAT practice; Economic Survey.
The Exam
June - Sept
Final Revision
Rapid revision of notes; Health maintenance; Mains Revision.
Key Principle: The entire syllabus (Prelims + Mains) implies a single integrated study unit. Do not segregate them initially.
During Preparation stay updated with UPSC Updates and Notifications.
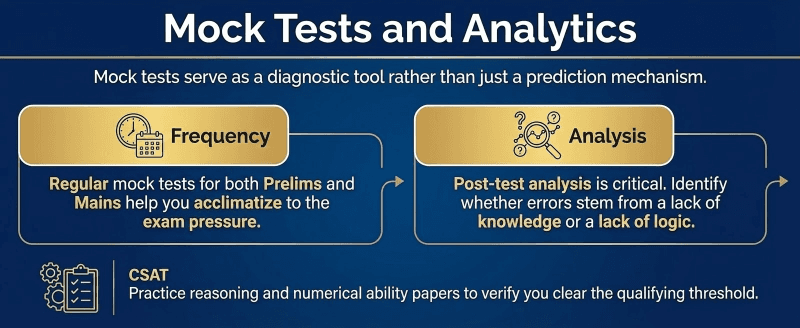
Step 8: Mock Tests and Analytics
Mock tests serve as a diagnostic tool rather than just a prediction mechanism.
Frequency: Regular mock tests for both Prelims and Mains help you acclimatize to the exam pressure.
Analysis: Post-test analysis is critical. Identify whether errors stem from a lack of knowledge or a lack of logic.
CSAT: Practice reasoning and numerical ability papers to verify you clear the qualifying threshold.
Step 9: The Personality Test (Interview)
The interview evaluates your intellectual integrity and social traits.
DAF Analysis: The Detailed Application Form (DAF) is the script of your interview. Know every word you wrote in it, from your hobbies to your graduation subjects.
Communication: Practice speaking clearly and confidently. Work on your body language and maintain eye contact.
Mock Interviews: Attend 3-4 mock interviews to receive external feedback on your demeanor.
Step 10: Mindset and Psychology
The UPSC journey is a marathon. Psychological resilience is as important as intellectual capacity.
Motivation: Surround yourself with a supportive environment. Take breaks to prevent burnout.
Discipline: Adhere to your study plan. Consistency beats intensity.
Talk Out Loud: Discuss topics with friends or yourself. This active recall technique reinforces memory linkages.
UPSC Strategy 2026
Optimization of Time and Strategy
Time acts as the most finite resource in the Civil Services Examination (CSE) cycle. An effective UPSC preparation strategy relies not on the number of hours invested, but on the intensity of focus and the "Cost of Retrieval" of information.
The 6-Month Compressed Cycle: For aspirants starting late, a how to prepare for upsc in 6 months strategy is viable but demands ruthlessness. You must bypass comprehensive reading and switch immediately to "reverse engineering" the exam. This involves analyzing UPSC syllabus and past question papers first. Also, you must maximize your chances by focusing heavily on high-yield subjects and current affairs during this compressed window.
Daily Architecture: Time management for upsc requires segregating the day into static core subjects (History, Polity) and dynamic current affairs. A methodical study routine, including a fixed timetable, combats stress and procrastination.
Be Consistent in UPSC Preparation: Success in CSE is cumulative. You must be consistent in upsc preparation by adhering to a routine that balances intensity with sustainability. Patience coupled with a methodical study plan yields better results than sporadic bursts of high effort. To maintain this, surround yourself with a supportive environment and incorporate physical activity to prevent burnout.
Resource Allocation: Analog vs. Digital
Books for UPSC Preparation: Your books must be limited to a "Bible list" to prevent information overload.
Core Texts: "Indian Polity" by M. Laxmikanth and "Indian Economy" by Ramesh Singh are non-negotiable.
Culture & History: "Indian Art and Culture" by Nitin Singhania and "India's Struggle for Independence" by Bipan Chandra,.
NCERTs: These remain the constitution of your study material, covering Classes 6-12.
Digital Integration: The modern aspirant leverages technology to reduce friction. A upsc preparation app or online platform can serve as a central repository for "Daily News Simplified" and current affairs summaries.
While the sources do not explicitly detail ai upsc tools, the shift toward "smart" preparation is evident in the recommendation to use online resources for real-time updates and test series. PadhAI.ai positions itself here, functioning as an intelligent filter for the vast ocean of data.
The Dilemma: Self Study vs Coaching The debate of self study vs coaching hinges on your personal discipline.
The Case for Coaching: Coaching is crucial for building a foundation and selecting the right reading materials.
The Case for Autonomy: Coaching is not mandatory. Many candidates succeed through self-study by relying on standard books and online resources.
Decision Matrix: If you require external discipline and structured testing, opt for coaching. If you possess high self-regulation, self-study suffices.
Academic Prerequisites and Exam Mechanics
Aspirants often ask which stream is best for upsc. The consensus is that while Humanities subjects (History, Political Science, Sociology) align naturally with the General Studies syllabus, any stream is suitable. Engineering and Medical graduates frequently clear the exam by choosing optional subjects that align with their logic-driven academic background or by learning a new humanities subject from scratch.
Rank Calculus: While the specific rank varies annually based on vacancies and reservation, generally, which rank is required for ias falls within the top 100 ranks for General category candidates to secure the Indian Administrative Service. Your rank depends heavily on the Mains score; thus, answer writing and optional subject performance are the deciding variables.
Risk Management: To mitigate negative marking in upsc, you must rely on the analysis of previous years' question papers. While the sources do not specify the deduction mechanics (classically 1/3rd marks), the strategy to counter this involves distinguishing between "calculated guesses" and "random attempts" during Mock Tests. Accuracy is prioritized over the number of attempts in the Preliminary stage.
Conclusion
The path to becoming a civil servant requires a synthesis of hard work, smart strategy, and emotional fortitude. By deconstructing the syllabus, mastering the NCERTs, and engaging in consistent answer writing, you transform an overwhelming challenge into a manageable process. As emphasized by top rankers, success implies not just reading, but revising and connecting the dots between static knowledge and the dynamic world. Start your journey today with the syllabus in one hand and a newspaper in the other.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. When should I start preparing for UPSC?
It is advisable to start preparing at least one to two years before the Preliminary Examination. This allows ample time for comprehensive coverage of the syllabus and revision.
Q2. How much time is required to prepare for IAS?
Dedicated study typically ranges from 1 to 2 years. This duration ensures you can cover the syllabus, practice answer writing, and revise effectively.
Q3. How do I prepare for the CSAT exam?
Understand the CSAT syllabus, which includes comprehension, reasoning, and numerical ability. Practice regularly with sample papers and previous years' question papers to improve speed and analytical skills.
Q4. Is coaching mandatory for UPSC preparation?
No. Coaching provides structure, but many candidates clear the exam through self-study by relying on standard books, online resources, and disciplined study plans.
Q5. What is the role of PadhAI in preparation?
PadhAI acts as "Knowledge Concentrators," providing access to AI doubt solving Tutor, Daily News Summaries and PYQ’s without the geographical constraints of physical coaching centers.